Not all GHG are created equal.
Though methane is shorter lived and less abundant than CO2, methane is over 80 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere in the short term.
Sustainable livestock farming is the management of animals in a way that meets current demands while not jeopardising the ability of future generations to do the same. It places a strong emphasis on sustainable practises, animal welfare, and financial viability. This strategy is essential because it tackles food security, limits resource depletion, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and supports the ethical treatment of animals—all of which are essential for a healthy planet and balanced ecosystems.
What role Cows play in Climate Change
According to FAO, the global livestock emissions amount to 7.1 GT of CO2e per year, representing 14.5% of all anthropogenic GHG emissions.
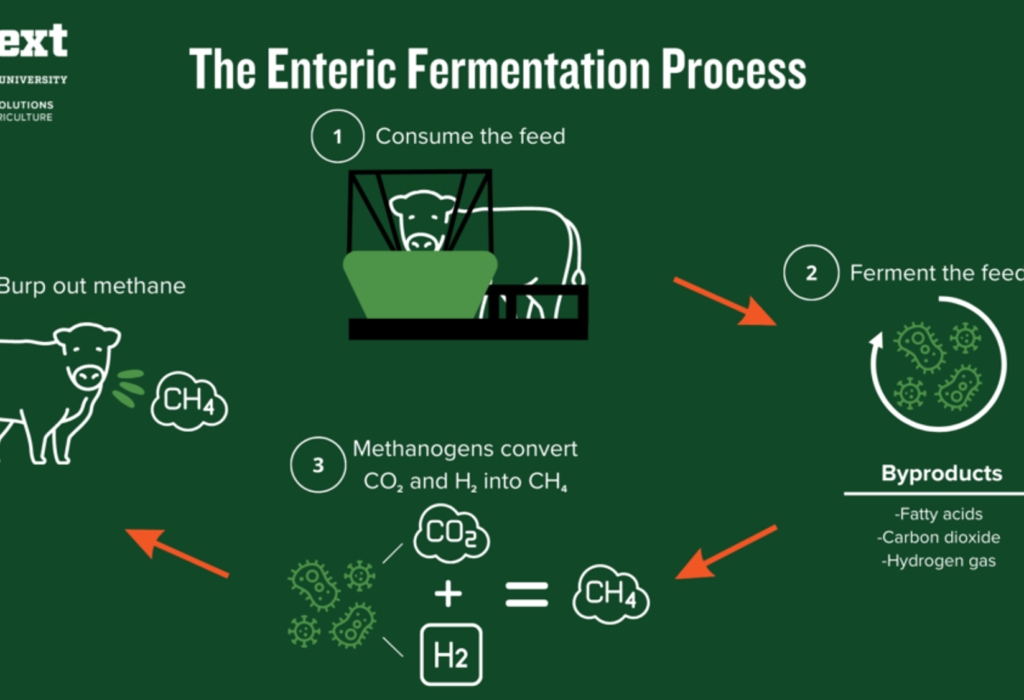



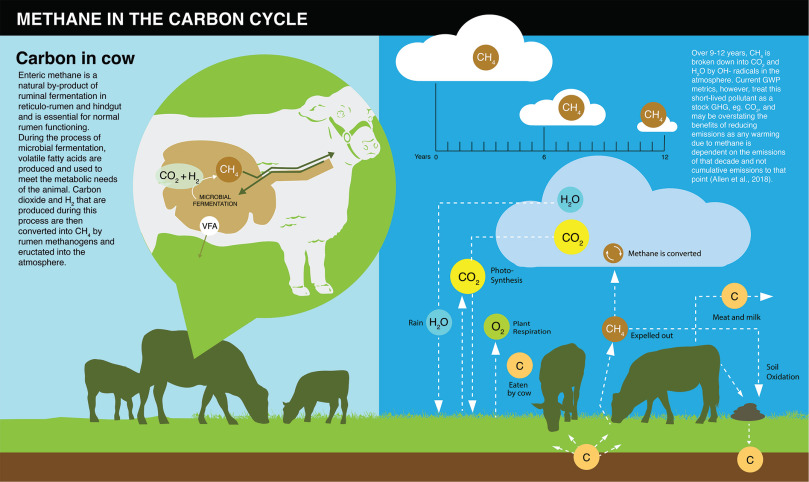
Enteric Fermentation
Ruminant animals like cows, buffaloes, sheep, goats and have stomachs/rumens that enables them to digest fibrous plant materials. During this digestion process, microbes in their stomach produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This methane is released into the atmosphere through belching. Belching accounts for more than 90 percent of the methane produced from livestock.
Manure Management
Livestock generates substantial amounts of manure. when improperly managed can release methane and nitrous oxide, another potent greenhouse gas. Methods like on-pasture farm management, composting, use as organic fertilizers, or use of manure to substitute it as paper or paint helps in better manure management which helps in reduction in methane production.
Land and Water Use
Livestock farming requires vast amounts of land for grazing and growing animal feed. This places pressure on ecosystems, leading to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss. Livestock energy consumes substantial amounts of water for drinking, cleaning and feed production. Water scarcity and pollution resulting from livestock operations are critical environmental concerns.
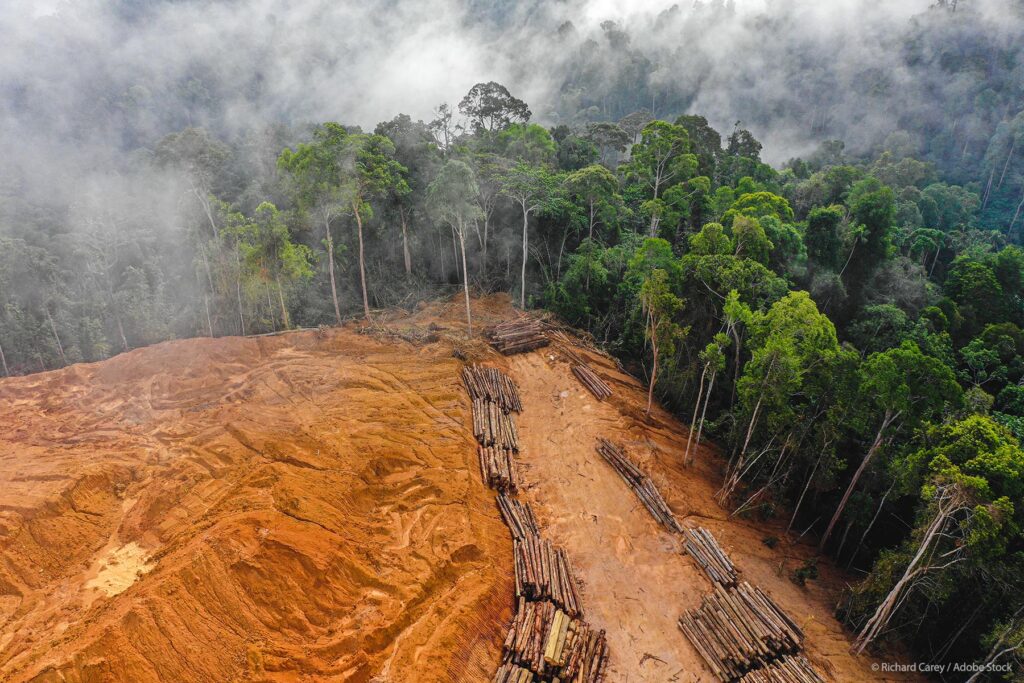
Deforestation & Agroforestry
Livestock production is a major driver of deforestation especially in tropical regions. Forests are cleared to create pastureland or to cultivate field crops for animals. Deforestation not only reduces the planet’s capacity to absorb CO2 but also releases stored carbon when trees are cut and burned.
What are the Sustainable Livestock Farming Practices?
Sustainable livestock farming is an approach to raising animals for food production that prioritizes environmental stewardship, social responsibility and economic viability. It aims to meet the current needs for animal-derived products while ensuring long-term health of ecosystems, communities and animal welfare.
Sustainable livestock farming involves practices that minimize negative environmental impacts, promote ethical treatment of animals, support local communities and maintain economic profitability for farmers.
Gentics
Considerations for choosing the right livestock breeds include the climate, the animal’s intended use (meat, milk, or labour), available resources locally, and market demands. Breeds with desired characteristics like disease resistance, high productivity, and effective resource use should be given priority. These breeds should also be tailored to the local climate. Breed selection that is adapted to regional conditions can improve cattle health, increase production effectiveness, and support sustainable agriculture and food security.
Nutrition
For the welfare of livestock and sustainable farming, proper animal nutrition and forage management are essential. It entails offering an animal a balanced diet that satisfies its unique nutritional requirements while taking into account the animal’s age, breed, and purpose. The cultivation, harvesting, and storage of premium feed supplies are all components of effective forage management. These methods improve the welfare of the animals, encourage productivity, lower expenses, and lessen the negative effects of livestock farming on the environment.
Waste Management
Minimising waste output, reusing resources, and recycling agricultural byproducts are all important components of efficient waste management and resource utilisation in agriculture. With this strategy, environmental contamination is decreased, precious resources like water and nutrients are preserved, and sustainability is promoted. Composting, crop residue integration, and precision irrigation are methods that help maximise resource utilisation, enhance soil health, and reduce farming’s ecological imprint, all of which assist ensure the long-term viability of agriculture.
Animal Welfare
Making sure animals are handled with respect and care is a part of ethical animal welfare issues in agriculture. This entails provide suitable housing, food, and medical attention in addition to reducing stress and pain. In order to promote humane treatment and accountable stewardship of cattle, ethical practises strive to strike a balance between human interests and the welfare of animals.
